More Than Just Addiction: Why Dual Diagnosis Care is Essential
Dual diagnosis is more common than most people realize. In fact, research finds that roughly half of all people with a mental illness will also struggle with addiction at some point. Among adolescents in addiction programs, over 60% meet the criteria for another psychiatric condition. In the US, about 21.5 million adults have a co-occurring disorder.
The most frequently linked mental health conditions include anxiety disorders, major depression, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and other psychiatric disorders. These mental health issues often fuel substance abuse (as people try to self-medicate painful symptoms), and vice versa – drugs and alcohol can trigger or worsen psychiatric symptoms.
Why Do Co-Occurring Disorders Happen?
Researchers explain that dual diagnosis arises partly from shared risk factors:
- Genetic vulnerabilities
- Changes in brain chemistry
- Early trauma or stress
In other words, there’s nothing mysterious preventing someone from having both kinds of disorders. For example, some people with depression or PTSD may turn to alcohol or drugs to cope, while certain substances (like stimulants or alcohol) can mimic or worsen symptoms of anxiety, depression, or psychosis.

As SAMHSA notes, “the coexistence of both a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder… is referred to as co-occurring disorders.” People with mental health conditions are at higher risk of developing addiction, and those with addictions are vulnerable to psychiatric illness.
The result is a vicious cycle: if one condition flares up, the other often does too. In fact, experts observe that untreated anxiety or depression tends to intensify substance use, and vice versa. In a nutshell, these co-occurring issues feel like playing “whack-a-mole” – you treat one problem and the other pops back up.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Co-Occurring Disorders?
Warning signs of co-occurring disorders often include symptoms of both addiction and mental health issues. For substance abuse, red flags can include:
- Sudden mood swings or secretive behaviors
- Declining work/school performance
- Frequent excuses for absences
- Physical signs like bloodshot eyes, tremors, or drastic weight changes may appear
- Social changes like new friend groups, unexplained financial problems, or legal troubles related to substance use are also common.
Likewise, untreated mental health conditions can manifest as persistent anxiety, deep depression, irritability, or sudden bursts of anger, often driving a person toward alcohol or drugs in an attempt to feel better. These overlapping symptoms underscore the need to consider both sides of the problem.
The Myth: “Get Sober First”
A dangerous myth is that someone must “get sober first” before addressing any mental health issues. In reality, experts warn this approach often fails. Simply staying clean doesn’t automatically resolve underlying psychiatric issues. Without integrated care, the untreated disorder usually resurfaces and drives a relapse.
What Integrated Dual Diagnosis Care Looks Like
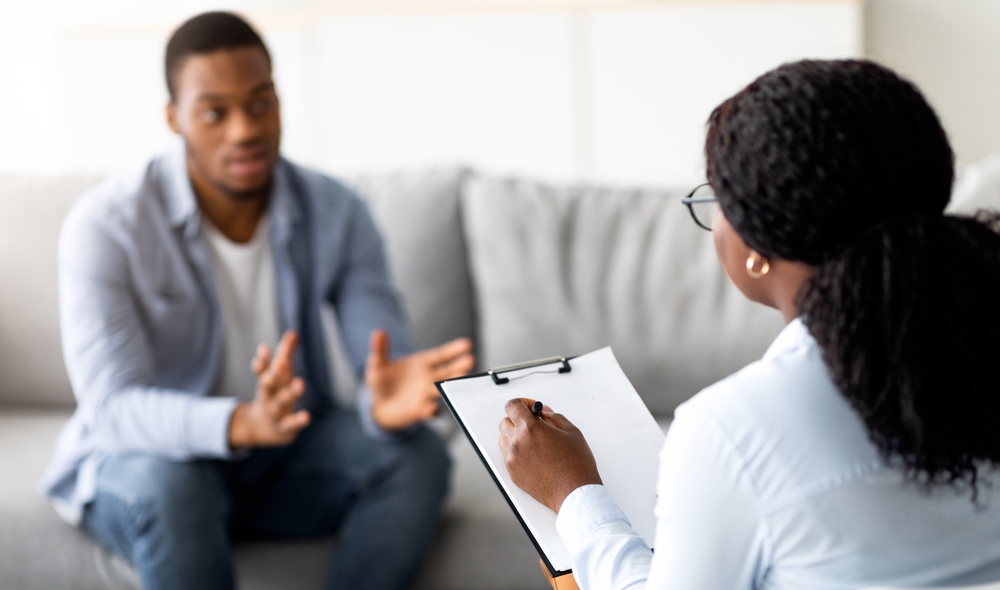

Dual diagnosis treatment typically involves one-on-one counseling and integrated therapies that address both addiction and mental health. Integrated care brings therapists and counselors together so that every treatment plan is tailored to the whole person, not just the addiction or just the depression.
For instance, dual diagnosis programs generally begin with a comprehensive psychiatric and substance abuse evaluation. This helps clinicians identify conditions like anxiety disorders, PTSD, bipolar disorder, or others alongside any substance use issues. Treatment often proceeds with a combination of behavioral therapies (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or dialectical behavior therapy) and medication management, all in a coordinated way.
Key Components of Dual Diagnosis Treatment
A core goal of dual diagnosis care is to teach healthier coping skills for the negative emotions and stressors that contribute to both problems. Therapy sessions (individual and group) help clients learn to recognize triggers for cravings and anxiety, and to practice skills like emotion regulation and relaxation.
Medical interventions, such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications, may be used alongside addiction medications (for example, buprenorphine or naltrexone) to stabilize brain chemistry. Importantly, medical detoxification is provided when needed: withdrawal from alcohol or sedatives can be dangerous, so patients are monitored 24/7 until they’re safely through the worst symptoms. This careful approach means clients can start treatment on solid footing rather than dropping out or relapsing due to unmanaged withdrawal symptoms or untreated depression.
What Dual Diagnosis Treatment Includes
Experienced programs use evidence-based behavioral therapies to treat both issues at once. Clients might attend group and family therapy sessions to build support, meet one-on-one with counselors, and work on relapse prevention planning.
Typical components include psychiatric care and medications to stabilize mood or anxiety, behavioral therapy (like CBT or motivational interviewing) to develop coping strategies, and support groups (such as AA/NA or SMART Recovery) for ongoing peer support. Patients and therapists also create a personalized relapse-prevention plan, focusing on how to handle triggers and distress without resorting to substances. Each plan emphasizes long-term recovery and teaches coping skills to deal with negative emotions in a healthy way.
Why Integrated Dual Diagnosis Care Works

The “gold standard” is to treat both disorders simultaneously in the same program. Integrated dual diagnosis care leads to better outcomes: studies find that clients who address mental health and addiction together use fewer substances over time and have fewer hospitalizations than those who treat only one disorder. By contrast, if only the drug or alcohol use disorder is treated, any lurking depression or PTSD will likely derail sobriety.
Integrated treatment avoids this trap. For example, specialized therapies like Integrated Group Therapy (IGT) for people with addiction and bipolar disorder or combined exposure/relapse-prevention therapies for PTSD and substance abuse have proven very effective. While more research continues, clinicians know that helping a person manage all their symptoms at once is far more successful than tackling issues in isolation.
Support and Aftercare
Recovery doesn’t end at discharge. Effective dual diagnosis programs often transition clients to outpatient support, sober living communities, or ongoing therapy to maintain gains. Peer support groups (AA, NA, SMART Recovery, etc.) and support from family play a lasting role. Education about warning signs and cravings helps patients activate coping strategies early.
For instance, relapse prevention plans might include identifying triggering negative emotions (like extreme stress or loneliness) and having ready alternatives (such as exercise, counseling, or 12-step meetings) to manage them. Patients also learn to recognize any warning signs of recurring mental health problems (for example, worsening sleep or mood), so they can seek help promptly. This comprehensive approach – combining medication, therapy, community support, and skills training – gives individuals the best chance for sustained, long-term recovery.
Take the Next Step with More Than Rehab
At More Than Rehab, we understand that dual diagnosis care is about healing the whole person. Our Texas-based programs treat mental health conditions and addiction together, with a warm, personalized approach. We offer evidence-based behavioral therapies, medical treatment for co-occurring disorders, family support, and peer groups to guide you through recovery.
If you or a family member has been dealing with substance abuse and an underlying psychiatric issue, our skilled team can help you build a relapse prevention plan and teach coping skills to regain control of your life. Call More Than Rehab (888-249-2191) or visit our website to learn about our integrated dual diagnosis programs. Recovery from both addiction and mental health issues is possible, and you don’t have to face it alone.