The Connection Between Chronic Pain, Opioid Use, & Mental Health
Chronic pain is more common and more misunderstood than many people realize. In the United States, nearly 50 million adults live with chronic pain. That’s one in five people waking up daily with discomfort that doesn’t go away.
If that’s you, you know it’s not “just pain.” It affects all aspects of your life – from sleep and energy to the ability to work, connect, and actually enjoy your life. It wears you down, physically and emotionally. And too often, the only solution offered by your doctor is a prescription drug.
For many, that prescription is an opioid. In the beginning, it helps. You might feel some relief, but over time, it stops working the same way. You may need a higher dose. You may start depending on it just to function. And slowly, without even realizing it, you're no longer managing pain – you’re managing your mind and body's dependence on the drug.
Understand Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is pain that doesn’t go away, even when doctors say you should be healed. It can show up after surgery, injury, or a health condition. Sometimes, there’s no clear reason. No test explains it. No scan shows it. And that can leave you frustrated and dismissed for months or even years.
The pain might be in your back, your neck, your joints, or deep in your nerves. It might stay in one spot or move around. Some days are better than others. But the hard days – the ones that steal your energy, focus, and joy, can pile up. It’s draining and a huge reason why most people with chronic pain also suffer from emotional issues.
Chronic Pain’s Impact on Mental Health

When you’re in pain for a long time, your nervous system stays in constant stress. The brain keeps receiving pain signals—even when the injury has healed, or there’s no clear reason for the pain. This continuous signal disrupts how your brain regulates mood, focus, and emotion.
Studies show that long-term pain alters the structure of the brain. It affects areas like the amygdala (which processes fear and anxiety), the prefrontal cortex (responsible for decision-making), and the hippocampus (which handles memory and emotional balance). These changes can lead to symptoms of depression, anxiety, and emotional numbness. You might notice you feel more anxious than usual. Or that it’s harder to stay motivated, focus, or find joy in things you used to love.
There’s also the hormonal side. Chronic pain activates your body’s stress system—the HPA axis. This leads to an increase in cortisol, your stress hormone. Elevated cortisol over time can worsen inflammation, disrupt your sleep, and lower your mood. It also reduces your body’s ability to manage pain naturally.
That’s why emotional struggles often go hand in hand with chronic pain. Research shows that depression is up to four times more likely in people with long-term pain. Anxiety disorders are also far more common.
And then there’s the social impact. Pain can interrupt your ability to work, stay active, or maintain relationships. That isolation creates more emotional strain. Many people living with chronic pain feel like they have to prove their experience. That lack of validation can add to emotional distress.
The Link Between Pain, Opioids, and Dependence
Opioids are often prescribed for chronic pain because they work fast. They block pain signals and release dopamine, a chemical that helps you feel calm and relaxed. For a while, you might feel like yourself again. But over time, your brain adapts.
It stops responding the same way. You build tolerance, meaning you need more of the drug to get the same relief. If you’ve been on opioids for a while, you might notice the dose that once worked doesn’t help much anymore. So you might need higher doses just to take the edge off.
But with higher doses come more side effects like constipation, brain fog, mood swings, and hormone issues. You may also notice that your pain doesn’t go away. It just gets masked for a little while. Then there’s the risk of opioid dependence, where your body starts to rely on the drug to function. If you skip a dose or try to stop, you might face withdrawal symptoms like anxiety, chills, or insomnia.
For some people, this leads to opioid misuse, even when the original goal was just to find relief. And the longer you’re on opioids, the greater the risk of accidental overdose, especially if you mix them with other medications or alcohol or if your health changes.
Research shows that 64.4% of people diagnosed with opioid use disorder (OUD) also live with chronic pain. And for most (about 61.8%), the pain comes first. Opioid use commonly begins as a treatment, but somewhere along the way, the drug ends up becoming the bigger problem. This is why long-term opioid therapy is no longer recommended as a first choice for most chronic pain. Not because your pain isn’t real. But because there are safer, more effective ways to manage it.
Stigma and Opioid Abuse
In the United States health care system, many people fear the label “drug-seeking” if they ask for stronger pain medication. Others worry they will be judged if they admit to feeling low or depressed. This stigma can prevent you from speaking openly with doctors, family, or friends. It can also keep you from finding the mental health services you need.
Stigma exists in two directions:
- Self-Stigma: Feeling ashamed of needing help for pain or mental health.
- Social Stigma: Others may label you as “addicted to painkillers” or weak if you use opioids or if you struggle with mood issues.
Breaking down stigma involves honest conversations with healthcare providers about pain management, potential opioid overdose prevention methods, and alternative therapies. It also involves acknowledging that chronic pain is real and deserves proper treatment.
Alternative Strategies for Pain Management
Chronic pain can be managed without over-relying on opioids. Approaches like physical therapy, gentle exercise, non-opioid medications, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can reduce pain and improve your ability to cope.
Other options such as mindfulness, nerve blocks, and simple lifestyle changes can help calm the nervous system and restore a sense of control. These strategies focus on long-term relief without the risks of dependence, making them safer and more sustainable tools for daily life.
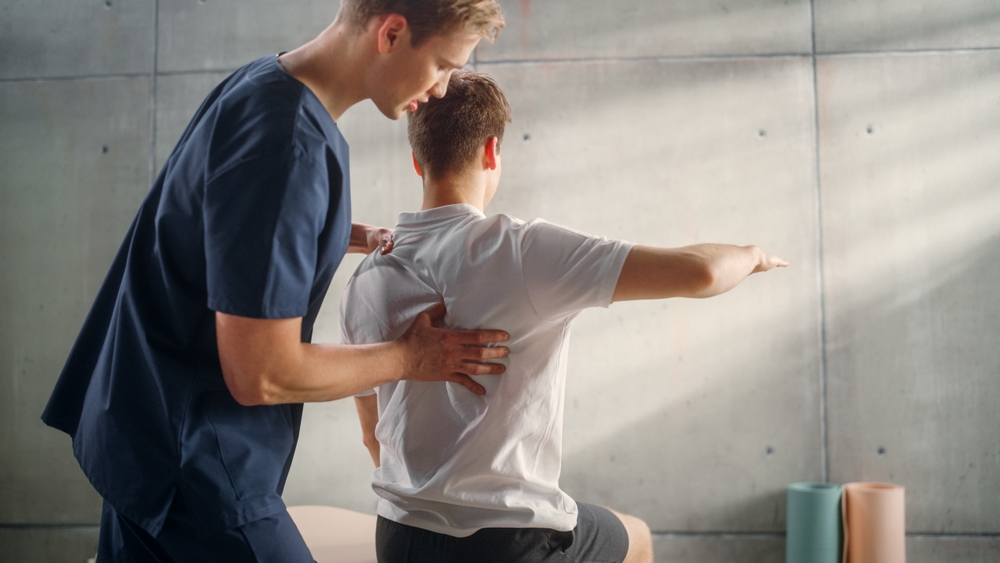

The Role of Integrated Care
If you’re managing both chronic pain and signs of substance abuse, integrated care brings everything together. You work with a team—doctors, mental health professionals, pain specialists—who create a plan tailored to your needs. This may include medication-assisted treatment (MAT) to reduce cravings, therapy to process emotional pain, and regular check-ins to track your progress. Integrated care treats your whole self—not just your symptoms—so you can break the cycle of pain, dependence, and isolation.
Opioid Addiction Treatment at MTR
At More Than Rehab, you’ll find comprehensive, whole-person opioid addiction treatment that honors your pain and helps you heal physically and emotionally. Whether you're seeking alternatives to opioids or support with addiction recovery, our team is here to guide you. Reach out to More Than Rehab today and take your next step toward lasting relief and recovery.